ActiveMQ Introduction
ActiveMQ is an open source (Apache 2.0 licensed) message brokerwhich fully implements the Java Message Service 1.1. It providesadvanced features like clustering, multiple message stores, andability to use file systems, and databases as a JMS persistenceprovider.
ActiveMQ HA
ActiveMQ support reliable high performance load balancing ofmessages on a queue across consumers. If a consumer dies, anyunacknowledged messages are redelivered to other consumers on thequeue. If one consumer is faster than the others it gets moremessages etc. If any consumer slows down, other consumers pick upthe slack. So you can have a reliable load balanced cluster ofconsumers on a queue processing messages.
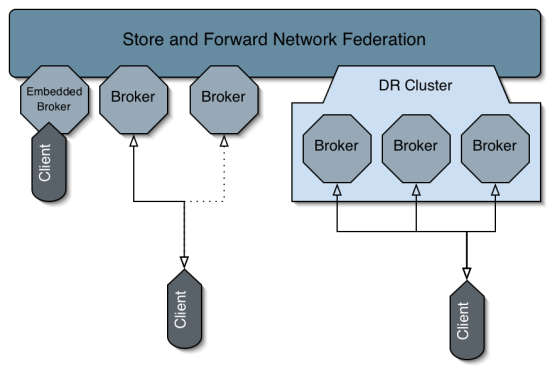
ActiveMQ support many types clustering, for example:
- Network of Brokers
- Advantage
- Networks of Brokers provides store and forward to move messagesfrom brokers with producers to brokers with consumers which allowsus to support distributed queues and topics across a network ofbrokers.
- The client uses failover protocol to connect to the network toachieve high performance.
- Disadvantage Messages are owned by a single physical broker at any point intime. If the broker goes down, the messages on this broker are notable to be consumed until the broker restarts again.
- Advantage
- Master/Slave
- Advantage Master/Slave provides a high availability mechanism. If themaster broker fails down one slave will take up the masterposition. Then the messages can always be insured to be deliveredto consumers unless all the brokers are down.
- Disadvantage At any time there is only one master that means all the timethere is only one broker which is working to receive and delivermessages. Then the performance should not be as good as network ofbrokers.
- A combination of Network of Brokers and Master/Slave
Reference
ActiveMQ topologies
ActiveMQ clustering
ActiveMQ:Networks of Brokers
ActiveMQ:Master/Slave
ActiveMQ:Transport configuration options
ActiveMQ:How do distributed queues work